01dragonslayer
Iron Killer
Mad Referrer
Jacked Immortal
EG Auction Sniper
VIP Member
Shout Master
Mutated
Fully Loaded
- EG Cash
- 1,113,693
 Will Brink, July 11, 2021, Articles, Bodybuilding, Strength Training, 0
Will Brink, July 11, 2021, Articles, Bodybuilding, Strength Training, 0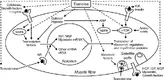
Editors Note: Concurrent training (explained below) has always been a controversial topic. Brooke covers the current science on the topic. I have discussed concurrent programing a number of times on this page over the years, and the Hybrid Program is a concurrent program, but I have not covered the science as Brooke does in this great guest article. Look for future articles from Brooke on BrinkZone.
Does Aerobic Training Interfere with Muscle Hypertrophy and Strength:
The Applied Science of Concurrent Training and Interference – By Brooke Morrisseau
 Brooke is obviously no stranger to the gym
Brooke is obviously no stranger to the gymThe inclusion of resistance training in combination with aerobic exercise in a single program is known as concurrent training (1). The “interference effect” stems from a paper by Hickson et al., which concluded that strength was hindered in response to concurrent training (10). The combination of resistance and endurance training may impair the adaptations associated with resistance training: strength, power development, and muscle hypertrophy (2). Interference suggests that concurrent training may attenuate strength, muscle mass (hypertrophy) and power, when compared to solely resistance training (8).
The research on concurrent training is by no means subjective. Although there is research concluding that concurrent training attenuates strength (1-4,7), and muscle hypertrophy(1,7) there is also research supporting that concurrent training contributes to strength and muscle hypertrophy (1,5, 6, 8).
What does “Concurrent Training” Mean ? How is it measured ?
Concurrent training studies typically have three separate groups: resistance
training only, endurance training only, and then resistance training and endurance training in the same program. Hickson et al. concurrent training protocol was 5 days of leg focused strength training, in combination with 6 days of endurance training: 3 days of interval training on an ergometer and 3 days a week of continuous running (30,35 and then 40 minutes progressively). Having concluded that resistance training adaptations are
attenuated when combined with endurance training, Hickson’s protocol did not account for individual fatigue (2).
Investigating adaptations to concurrent training is not universal,
as there are a multitude of variables that can be manipulated. Individual training status, and measures used to assess strength and hypertrophy also play a role in concurrent training study results and conclusions.
Are you trained or untrained ? It matters!
Individual training status can influence training adaptation, post-exercise
responses, and long-term adaptations to training resistance training. Much of the research on concurrent training involves untrained subjects. Untrained individuals have an enhanced capacity for adaptation, when being compared to trained individuals, which is supported by the law of diminishing returns (2). Untrained subjects will likely respond
differently to a concurrent training intervention, when analyzing hypertrophy and strength, in comparison to individuals who are resistance or endurance trained (2).
What is the mechanism of muscle growth ? Strength ?
Muscle hypertrophy is thought to be mediated by the activity of satellite cells, and the actual muscle growth aspect results from an increase of sarcomeres and myofibrils being added in parallel (10). For an untrained individual, muscle hypertrophy typically does not occur within the first few weeks of resistance training. Gains in strength for an untrained individual result in the initial neural adaptations being made (9). Although there is research to support that concurrent training attenuates muscle strength and size, there are no studies investigating or observing the molecular
interference that follows concurrent training. Mechanistic implications showing specific molecular signaling responses induced in skeletal muscle by endurance exercise may provide potential mechanistic implications on the interference effect following concurrent training, in relation to muscle hypertrophy and strength.
Key Points:
● A program that includes the combination of resistance and aerobic training istermed concurrent training.
● Although there is evidence that concurrent training can attenuate muscle growth and strength, there is also conflicting evidence that supports impairing muscle growth and strength.
● Most of the evidence is on untrained subjects. If you are untrained, then this will apply to you. If you are trained in endurance or resistance training, or both, then the research is limited.
● Do not fear aerobic training. Program a combination of resistance and aerobic training to suit your individual goal. Approach this with intentionality and follow a progression scheme over a period of time to prevent overtraining or high levels of fatigue.
● Although the literature evaluates concurrent training from a macro- based scale,there are no mechanistic implications or understanding on the interference effect from the current literature. Future work to understand the mechanism behind interference needs to be done. It is important to note the level of detail that goes into these research studies, and we must show appreciation to the work that has
been done.
Applications:
● Incorporate both resistance and aerobic training (concurrent training), tailored toward your individual goal.
● Choose one main focus area, such as aerobic training or strength / hypertrophy training, and have your program tailored toward that first. We can not be an olympic long distance runner and a professional bodybuilder at the same time…choose one, and then go all in on that!
● Identify if you are untrained or trained, then you can use the literature to evaluate your own individual needs.
● Use “the science” as a guide, but understand that what is “the best way” ultimately will be individual to you.
About Brooke:
Brooke Morrisseau: Is currently perusing a Masters of Science- Exercise Physiology at University of South Florida and her many articles, vids, and fitness/training advice can be found: The Physique Scientist








